Jaggery, often called “gur” in Hindi, is a traditional sweetener widely used in South Asia, Latin America, Africa, and the Caribbean. It is derived from the sap of various plants, such as sugarcane, date palm, and coconut. Making involves boiling the sap until it solidifies into blocks or cakes. This natural sweetener has been a staple in various cuisines for centuries, prized not only for its sweetness but also for its distinct flavor and nutritional benefits.
Types and Categories
| Type of Jaggery | Source Plant | Production Method | Region of Origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Palm Jaggery | Palm trees | Traditional | South and Southeast Asia |
| Cane Jaggery | Sugarcane | Traditional/Commercial | Worldwide |
| Date Jaggery | Date palm | Traditional | Middle East, North Africa |
Amazing Health Benefits of Jaggery
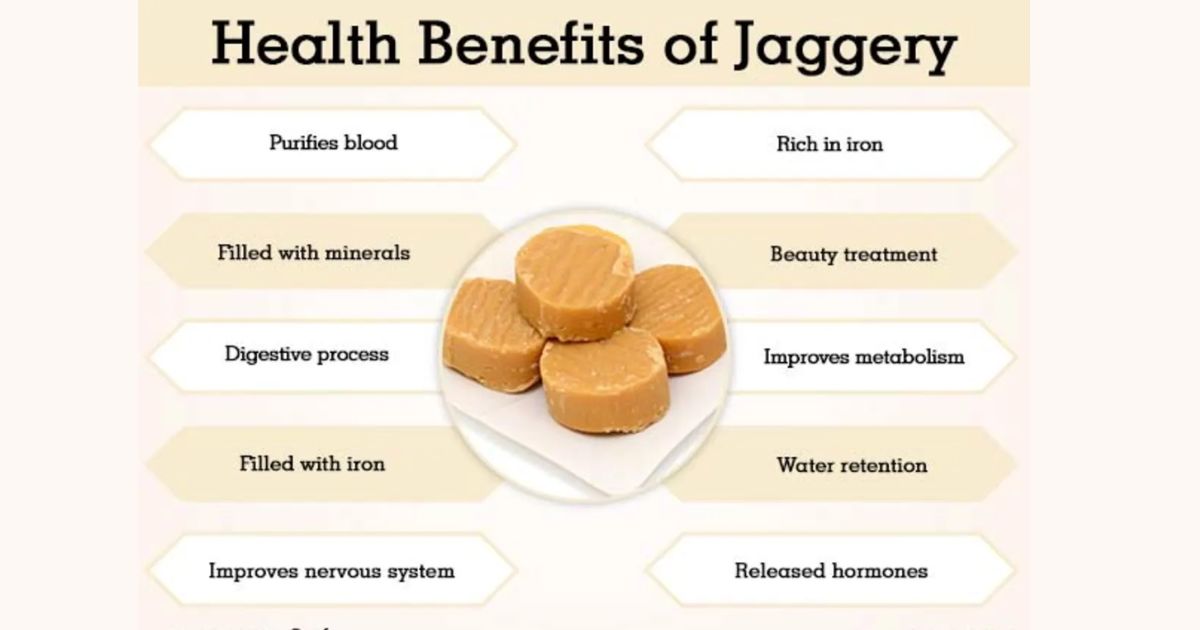
Despite its high sugar content is prized for its nutritional richness. It contains various vitamins and minerals, including iron, magnesium, potassium, and calcium. Unlike refined sugar, which is stripped of nutrients during processing, retains these essential micronutrients, making it a healthier alternative. Moreover, it has a lower glycemic index compared to white sugar, which means it causes a slower and steadier rise in blood sugar levels.
1. The Powerhouse of Vitamins and Minerals
One of the most compelling aspects of jaggery is its rich nutritional composition. Packed with essential vitamins and minerals, including iron, magnesium, potassium, and vitamins A, B, and C, jaggery offers a holistic approach to health and vitality. Iron, in particular, plays a vital role in combating anemia, making jaggery a valuable addition to diets worldwide. With its potent blend of nutrients, jaggery stands as a beacon of nourishment in an era marked by processed foods and empty calories.
2. Culinary Uses
In culinary applications, adds a distinct flavor and sweetness to dishes. It is commonly used in traditional sweets and desserts across various cultures. From Indian delicacies like “gur ki kheer” and “gulab jamun” to Latin American treats like “dulce de leche,” finds its way into a myriad of recipes. Furthermore, it is used in beverages such as “chai” (Indian tea) and “agua de panela” (Latin American hot drink). Moreover, it is gaining popularity as a healthier alternative to refined sugar in baking and cooking, especially in vegan and gluten-free recipes.
3. Balancing Blood Sugar Levels
Contrary to popular misconceptions about sugar, jaggery possesses a unique ability to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. Its complex carbohydrates release glucose slowly into the bloodstream, preventing sudden spikes and crashes in blood sugar. This gentle modulation not only helps in managing diabetes but also promotes sustained energy levels throughout the day. By choosing jaggery over refined sugar, individuals can indulge their sweet tooth without compromising their health, making it a win-win solution for all.
4. Purifies Blood
One of the most popular benefits of Jaggery is that it has the ability to purify the blood. If consumed regularly, helps a lot in purifying the blood and keeping the body healthy. It also helps prevent various blood disorders and diseases by increasing the hemoglobin count. Jaggery also boosts immunity and thus helps in preventing various blood related problems.
5. Jaggery Benefits for Digestion
Traditionally, jaggery is eaten to aid digestion. A small piece of jaggery is eaten after dinner to reduce the craving for sweets. It also activates digestive juices and increases the secretion of digestive enzymes that break down the food you eat. Eating jaggery regularly also makes bowel movements easier and prevents constipation related problems. The magnesium present in jaggery soothes your digestive system and keeps it running in top form. Do you know? That 10 grams of jaggery gives you 16mg magnesium.
6. Alleviating Menstrual Discomfort
For many women, menstrual discomfort is an unwelcome monthly visitor that disrupts daily life and productivity. Fortunately, jaggery offers a natural remedy for alleviating menstrual cramps and discomfort. Its iron-rich composition helps in replenishing lost blood and alleviating symptoms of fatigue and weakness often associated with menstruation. Additionally, jaggery’s warming properties help in soothing abdominal muscles and reducing pain intensity, providing much-needed relief during that time of the month.
7. Energy Booster
Palm Jaggery is a complex carbohydrate. You may digest it slower than white sugar. It is digested slowly and hence releases energy when consumed. This means that after eating date jaggery, you can get more energy and remain active for hours.
Myths and Misconceptions
Despite its many health benefits is often subject to myths and misconceptions. One common misconception is that jaggery is a suitable alternative for individuals with diabetes. While it does have a lower glycemic index compared to white sugar, it still raises blood sugar levels and should be consumed in moderation by individuals with diabetes. Another myth is that is a healthier option for weight loss. While it may contain more nutrients than refined sugar, still high in calories and should be consumed as part of a balanced diet.
Buying Guide
When purchasing jaggery, it’s essential to consider factors like quality, purity, and sourcing. Look for organic or certified jaggery products to ensure they are free from chemical additives and pesticides. Opt for jaggery that is dark brown or golden, as lighter shades may indicate impurities or excessive processing. Additionally, buying directly from local producers or trusted brands can ensure authenticity and support small-scale farmers. Store in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight to prevent it from melting or crystallizing.
Health Risks and Precautions
While jaggery offers numerous health benefits, excessive consumption can have adverse effects. Like any sweetener, jaggery is high in calories and can contribute to weight gain if consumed in large quantities. Individuals with diabetes should monitor their intake and consult with a healthcare professional to determine suitable portion sizes. Moreover, some people may experience allergic reactions or digestive issues due to jaggery consumption. It’s essential to listen to your body and discontinue use if any adverse reactions occur.
FAQs
Ans. It is made by boiling the sap of plants like sugarcane or palm, whereas brown sugar is refined white sugar with molasses added back in.
Ans. Yes, can be used as a substitute for white sugar in baking, but it may alter the taste and texture of the final product.
Ans. While it has a lower glycemic index than white sugar, it still raises blood sugar levels and should be consumed in moderation by individuals with diabetes.
Ans. It contains more nutrients than honey and maple syrup but is higher in calories. Each sweetener has its unique flavor profile and culinary uses.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Jaggery is not just a sweet indulgence but also a nutritious addition to a balanced diet. Its rich flavor, health benefits, and environmental sustainability make it a preferred choice for many consumers seeking healthier alternatives to refined sugar. By understanding its nutritional profile, culinary uses, and potential health risks, individuals can enjoy the sweetness while making informed dietary choices.