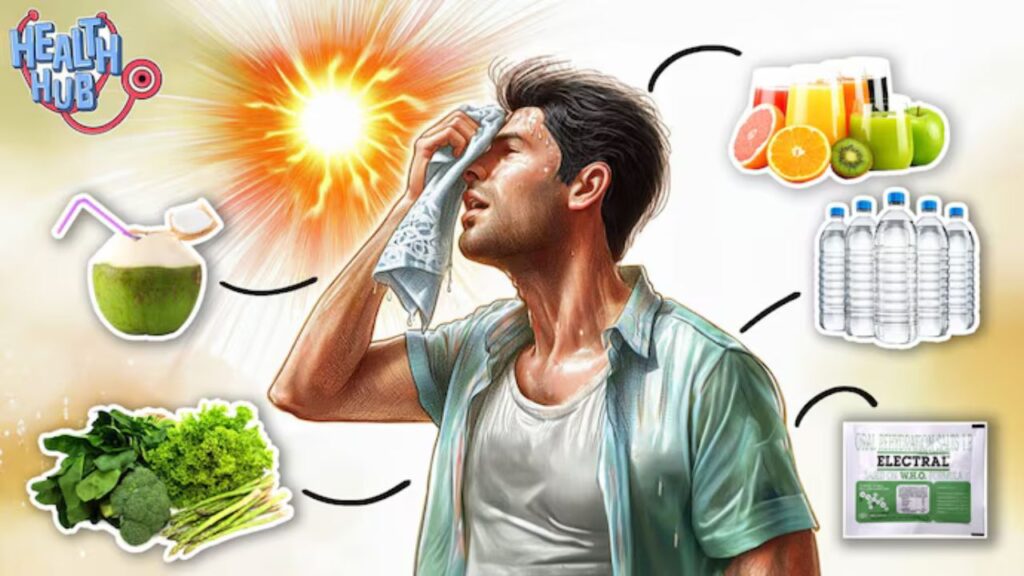
Hydration refers to the process of maintaining an adequate level of water and electrolytes in the body. It is crucial for various bodily functions, including temperature regulation, joint lubrication, and the transport of nutrients and waste. Hydration is essential for maintaining overall health, especially during extreme conditions such as heatwaves.
Relevance of Proper Hydration During Heatwaves
Proper hydration becomes critically important during heatwaves. The body loses more water through sweating as it tries to cool down, leading to a higher risk of dehydration. Dehydration can exacerbate heat-related illnesses, including heat exhaustion and heatstroke. Therefore, understanding and maintaining proper hydration can be a key factor in surviving severe heatwaves.
Understanding Hydration
What is Hydration?
Hydration involves the intake and regulation of fluids in the body. It is not just about drinking water but also about maintaining a balance of electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and chloride, which are essential for bodily functions.
The Role of Water in the Body
Water is vital for numerous physiological processes. It helps regulate body temperature, aids in digestion, transports nutrients, and removes waste products. The human body is composed of approximately 60% water, making it essential for life.
Importance of Electrolytes
Electrolytes are minerals that carry an electric charge and are found in body fluids. They are crucial for various bodily functions, including nerve transmission, muscle contraction, and maintaining fluid balance. Without adequate electrolytes, even with sufficient water intake, the body cannot function optimally.
Types and Categories of Hydration
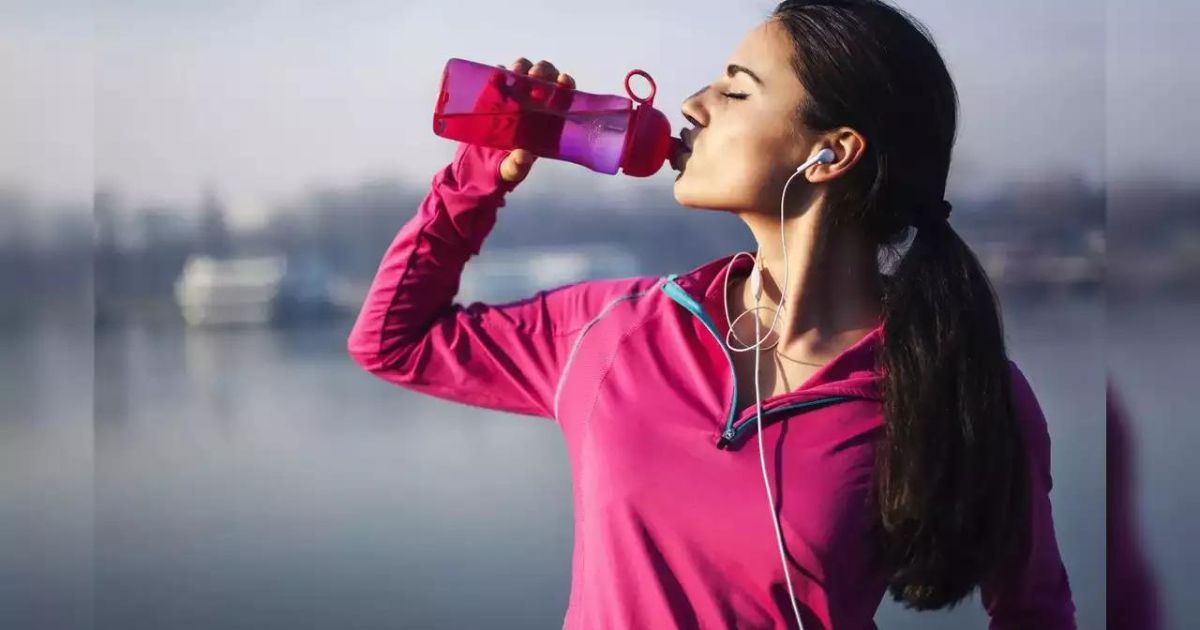

Oral Hydration
-
Water
Water is the most basic and essential form of hydration. It is crucial for replenishing fluids lost through sweating, breathing, and urine.
-
Electrolyte Solutions
Electrolyte solutions, such as oral rehydration salts (ORS), are designed to replenish both fluids and electrolytes lost during dehydration. They are particularly useful during heatwaves when sweat loss is high.
-
Sports Drinks
Sports drinks contain electrolytes and carbohydrates. They are formulated to rehydrate and provide energy during prolonged physical activities. However, they can contain high levels of sugar and should be consumed in moderation.
-
Intravenous Hydration
Intravenous (IV) hydration involves the direct infusion of fluids and electrolytes into the bloodstream. It is used in severe cases of dehydration or when oral hydration is not possible.
-
Hydration
Supplements
Hydration supplements, such as electrolyte tablets or powders, can be added to water to enhance its hydrating properties. They are convenient for maintaining electrolyte balance during intense activities or heat exposure.
Symptoms and Signs of Dehydration
Common Symptoms
- Thirst– Thirst is the body’s natural signal indicating the need for water. It is the most immediate and recognizable symptom of dehydration.
- Dry Mouth– A dry or sticky feeling in the mouth is another early sign of dehydration.
- Dark Urine– Dark yellow or amber-colored urine indicates a high concentration of waste products due to insufficient water intake.
Severe Symptoms
- Dizziness– Dizziness or lightheadedness can occur when dehydration reduces blood volume and pressure, affecting blood flow to the brain.
- Rapid Heartbeat– A rapid or irregular heartbeat may result from the body’s effort to maintain blood pressure despite lower fluid levels.
- Confusion– Confusion, irritability, or lack of coordination can occur in severe dehydration, affecting cognitive function and overall mental state.
Treatment Options for Dehydration
Oral Rehydration Solutions
Oral rehydration solutions (ORS) are a simple and effective treatment for dehydration, especially in mild to moderate cases. They provide a balanced mixture of salts and sugars to aid absorption.
Intravenous Fluids
In severe dehydration or when oral intake is not possible, intravenous (IV) fluids can rapidly restore fluid and electrolyte balance.
Electrolyte Supplements
Electrolyte supplements, such as tablets or powders, can help maintain or restore electrolyte balance, especially during high fluid loss conditions.
Conclusion
Hydration is essential for survival during heatwaves. Proper hydration involves maintaining a balance of water and electrolytes to support bodily functions and prevent dehydration. Recognizing early signs of dehydration and adjusting fluid intake based on environmental conditions and physical activity are crucial strategies.